Financial Instruments (FI) essentials for Managing Authorities and Implementing bodies on how to design and implement FI under ESIF 2014-2020
What are the Financial Instruments under ESI Funds
The Cohesion Fund and the Structural Funds are financial tools set up to implement the regional policy of the European Union. They aim to reduce regional disparities in terms of income, wealth and opportunities.

The 5 European Structural and Investment Funds may be used to support FI under one or more programs’, including when organized through funds of funds, in order to contribute to the achievement of specific objectives set out under a priority
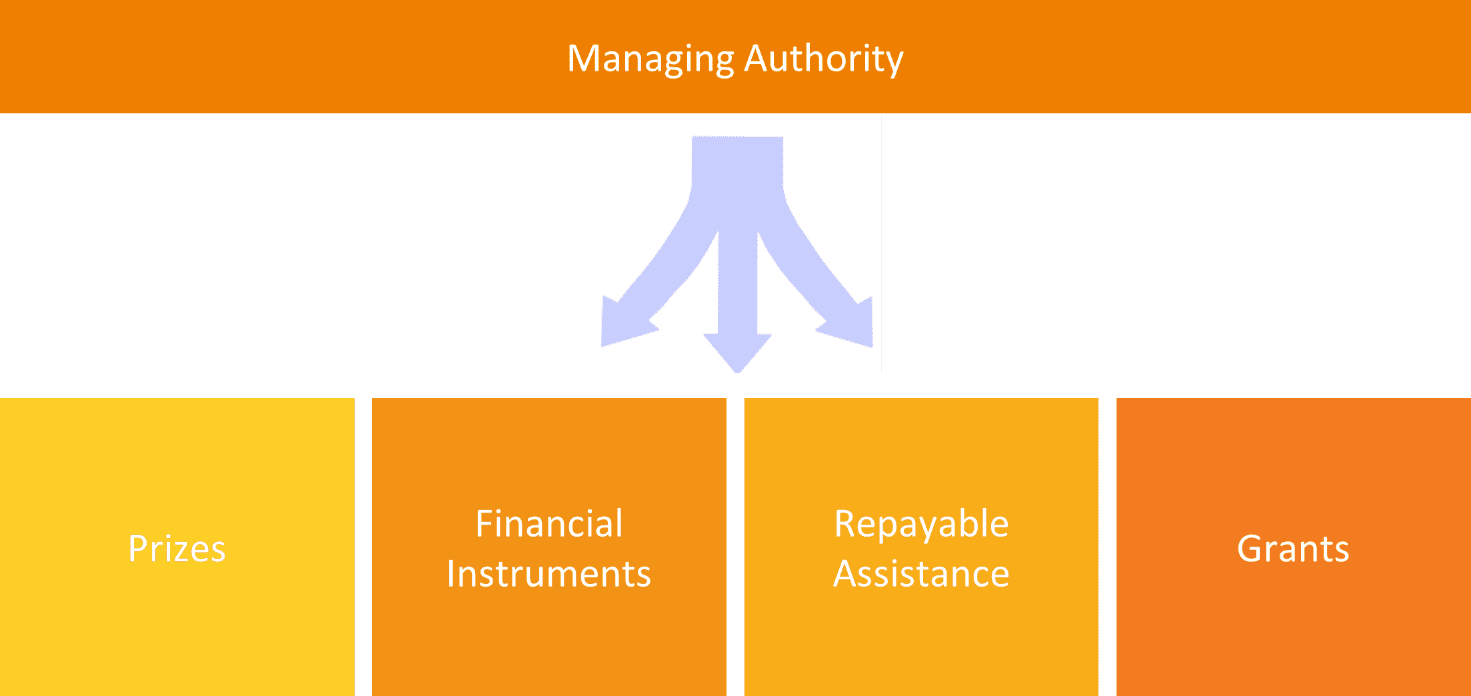
Financial instruments under the ESI Funds are Union measures of financial support provided on a complementary basis from the budget in order to address one or more specific policy objectives of the Union. Such instruments may take the form of equity or quasi‑equity investments, loans or guarantees, or other risk‑sharing instruments, and may, where appropriate, be combined with grants.
Financial Instruments in pills
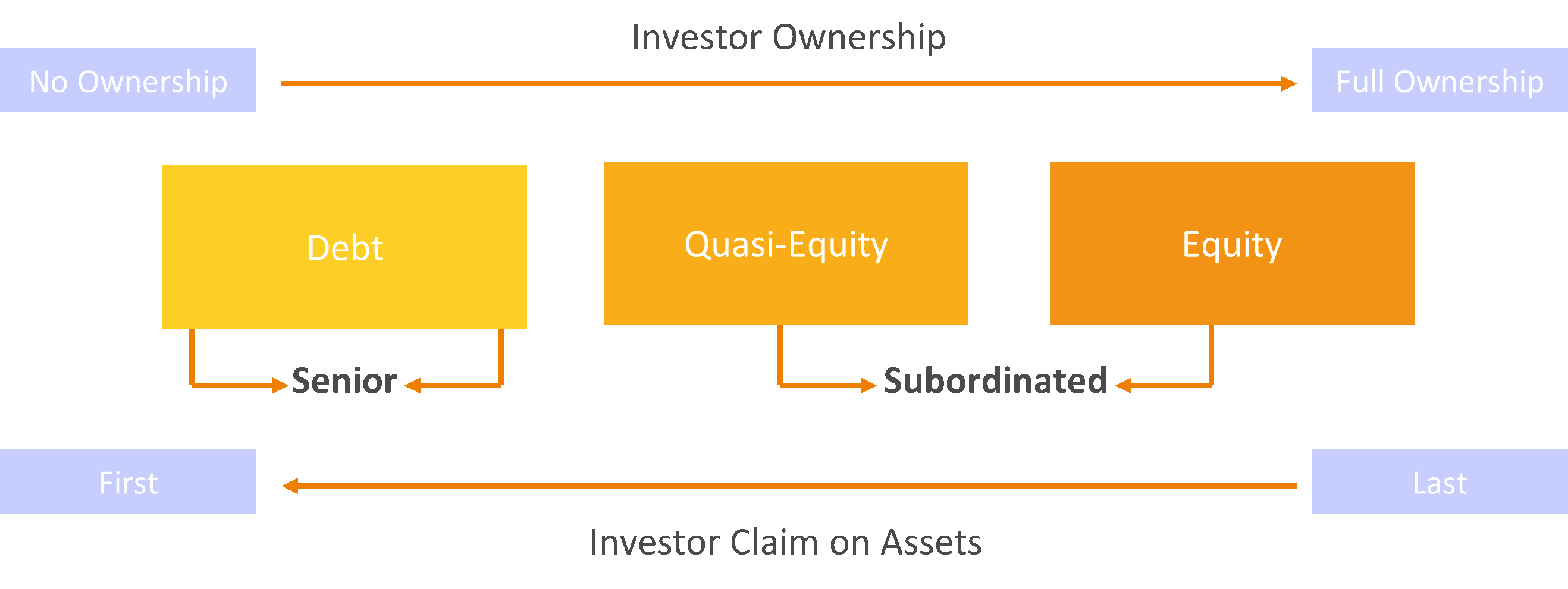
Equity investment – the provision of capital to a firm, invested directly or indirectly in return for total or partial ownership of that firm and where the equity investor may assume some management control of the firm and may share the firm’s profits.
Quasi-equity investment – a type of financing that ranks between equity and debt, having a higher risk than senior debt and a lower risk than common equity. Quasi‑equity investments can be structured as debt, typically unsecured and subordinated and in some cases convertible into equity, or as preferred equity.
Loans – an agreement which obliges the lender to make available to the borrower an agreed sum of money for an agreed period of time and under which the borrower is obliged to repay that amount within the agreed time.
Guarantees – a written commitment to assume responsibility for all or part of a third party’s debt or obligation if an event occurs which triggers such guarantee, such as a loan default.
The rise of Financial Instruments in the political strategy
October 2012
The Europe 2020 strategy and the Commission Communication on the MFF 2014-2020 called for a stronger role of FI in 2014-2020.
October 2013
The European Council conclusions subsequently gave a clear mandate that the programming negotiations of the European Structural and Investment Funds (ESIF) should be used to “significantly increase the overall EU support from these funds to leverage-based FI for SMEs in 2014-2020, while at least doubling support in countries where conditions remain tight.”
November 2014
The “Investment Plan for Europe” invited Member States to increase significantly their use of innovative financial instruments in key investment areas in order to achieve at least an overall doubling in their use.
2015
The new European Structural and Investment Funds (ESIF) legal framework facilitates and encourages the use of financial instruments. It broadens the scope of financial instruments (opening them to all thematic objectives) and offers a variety of different implementation options.
Financial Instruments in practice
Member States and regional governments can use European Structural and Investments funds (originated from the EU Budget) to finance seven-year economic and social development strategies. Regional strategies must be in line with the broader “Europe’s 2020 growth and jobs strategy”, their Smart Specialization Strategy and will result in Operational Programme negotiated and approved by the European Commission.
In designing the operational programmes Member States and regions will define priority axes related to one or more priorities among the 11 thematic objectives of the Europe 2020 strategy.
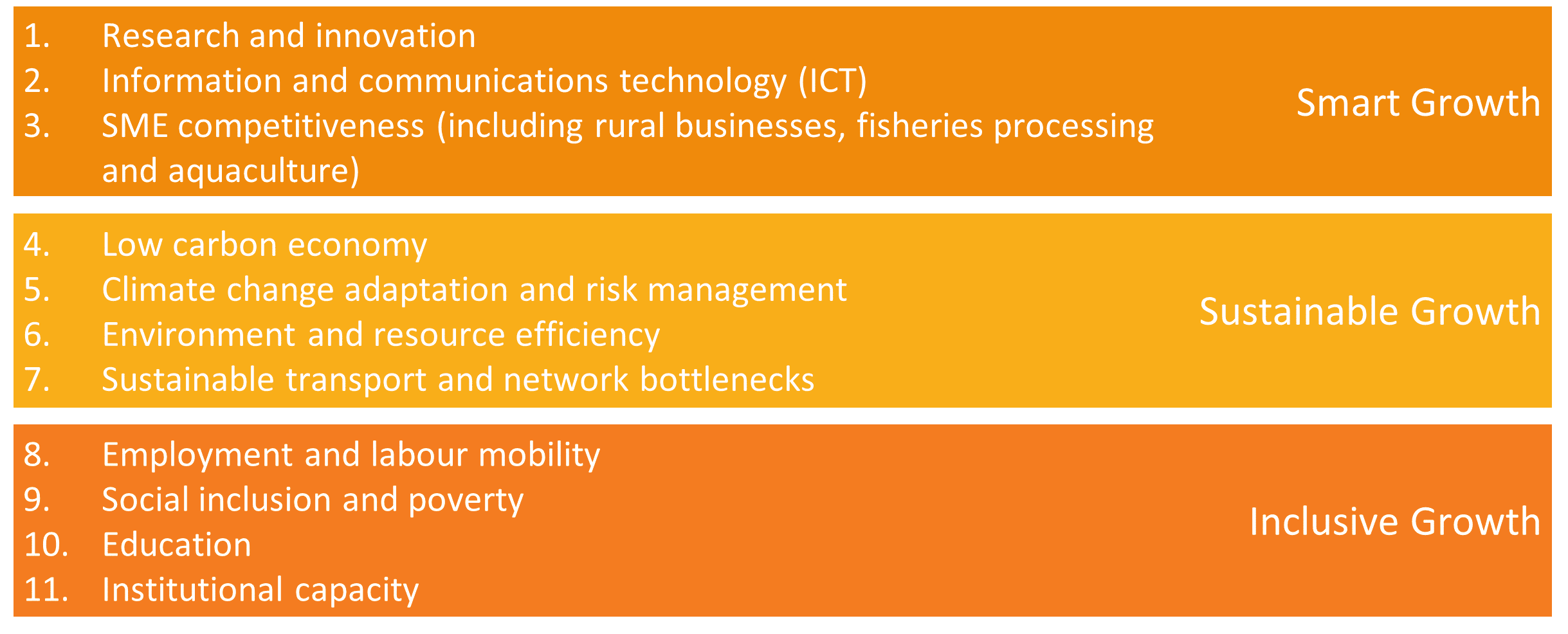
Managing Authorities can establish financial instruments, under one or more priority axes, to encourage and support the most promising projects available in their markets.
Financial instruments are meant to support solely investments that are expected to be financially viable but are unable to raise sufficient funding due to market failures or poor availability of specialized finance.
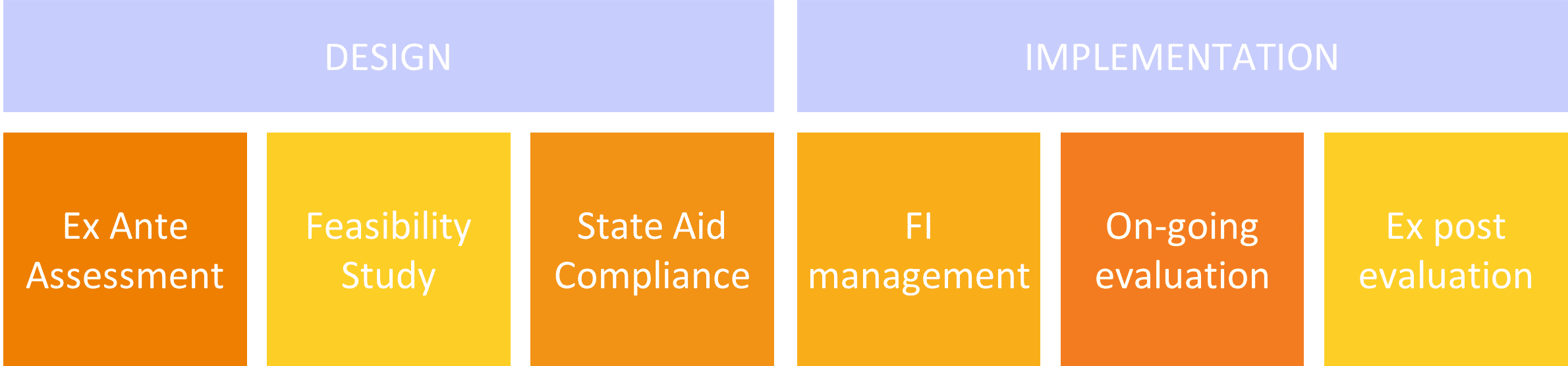
Establishment of financial instruments shall be based on a compulsory ex ante assessment which shows evidence of market failures or suboptimal investment situations, disclosing the estimate level and scope of public investment needs, including types of financial instruments to be supported.
META solutions for ESI Funds Managing Authorities and Implementing Bodies
The wide portfolio of options offered under the ESI framework requires Managing Authorities to focus on planning, designing and managing new financial instruments capable at the same time to tackle the regional specificities and to contribute to the achievement of the Programme and the ESI Funds objectives.
META’s solutions are designed around the needs of Managing Authorities and Intermediate Bodies willing to create efficient financial instruments, compliant with national and EU laws, based on the international market requirements.
With over 20 years of experience in designing and implementing equity financial instruments at European level, META can offer the following services:
For more information please contact us

